 A bacteriophage is any of a group of viruses that infect bacteria. Bacteriophages were discovered independently by Frederick W. Twort in Great Britain (1915) and Felix d’Herelle in France (1917). Thousands of varieties of phages exist. Certain types serve key roles in laboratory research.
A bacteriophage is any of a group of viruses that infect bacteria. Bacteriophages were discovered independently by Frederick W. Twort in Great Britain (1915) and Felix d’Herelle in France (1917). Thousands of varieties of phages exist. Certain types serve key roles in laboratory research.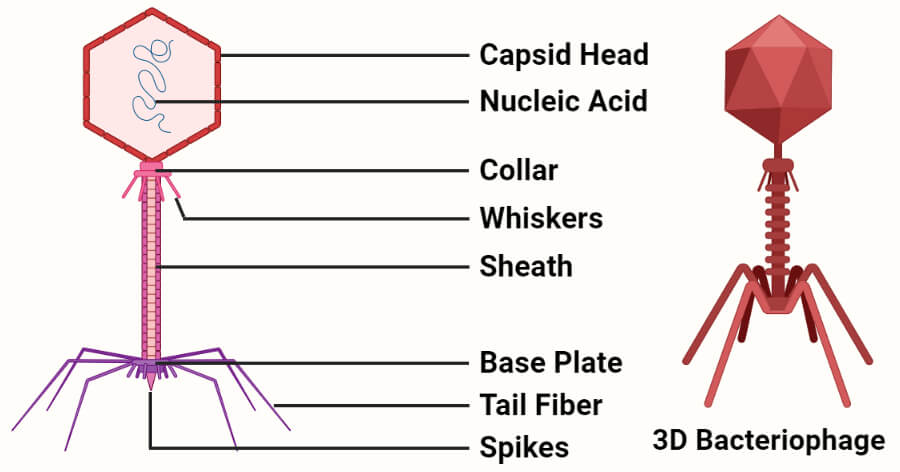 Bacteriophage or Phage is a virus that infects and replicates only within the body of bacteria. Bacteriophages were discovered independently by Frederick W. Twort in the U.K and Félix d’Hérelle in France.
Bacteriophage or Phage is a virus that infects and replicates only within the body of bacteria. Bacteriophages were discovered independently by Frederick W. Twort in the U.K and Félix d’Hérelle in France. Bacteriophages “bacteria-eater” are infectious agents that replicate as obligate intracellular parasites in bacteria with high selectivity. They are the powerful regulators of bacterial populations in natural ecosystems and are found in the soils, plants, rivers, and also as the human microbiome.
Bacteriophages “bacteria-eater” are infectious agents that replicate as obligate intracellular parasites in bacteria with high selectivity. They are the powerful regulators of bacterial populations in natural ecosystems and are found in the soils, plants, rivers, and also as the human microbiome.